Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences.
Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Answer Key Estimate Fraction Sums and Differences
Unlock the Problem
Kimberly will be riding her bike to school this year. The distance from her house to the end of the Street is \(\frac{1}{62}\)mile. The distance from the end of the Street to the school is \(\frac{3}{8}\) mile. About how far is Kimberly’s house from school?
You can use benchmarks to find reasonable estimates by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
One Way:
Use a number line.
Estimate. \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
STEP 1:
Place a point at \(\frac{1}{6}\) on the number line.
The fraction is between ________ and __________.
The fraction \(\frac{1}{6}\) is closer to the benchmark _________.
Round to ________.
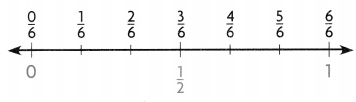
STEP 2:
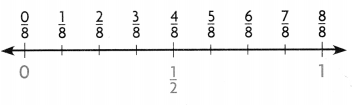
Place a point at \(\frac{3}{8}\) on the number line.
The fraction is between __________ and _________.
The fraction \(\frac{3}{8}\) is closer to the benchmark ___________.
Round to _________.
STEP 3:
Add the rounded fractions.
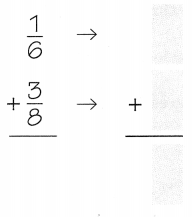
So, Kimberly’s house is about ________ mile from the school.
Answer:\(\frac{1}{6}\)
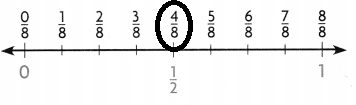
Use a number line.
Estimate. \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
STEP 1:
Place a point at \(\frac{1}{6}\) on the number line.
The fraction is between \(\frac{0}{6}\) and \(\frac{6}{6}\)
The fraction \(\frac{1}{6}\) is closer to the benchmark \(\frac{0}{6}\)
Round to \(\frac{0}{6}\)
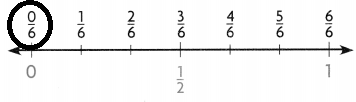
STEP 2:
Place a point at \(\frac{3}{8}\) on the number line.
The fraction is between \(\frac{0}{8}\) and \(\frac{3}{8}\)
The fraction \(\frac{3}{8}\) is closer to the benchmark \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Round to \(\frac{4}{8}\)
STEP 3:
Add the rounded fractions.
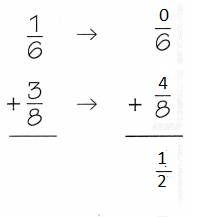
So, Kimberly’s house is about \(\frac{1}{2}\)mile from the school.
Another Way
Use mental math.
You can compare the numerator and the denominator to round a fraction and find a reasonable estimate.
Estimate. \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\)
STEP 1:
Round \(\frac{9}{10}\).
Think: The numerator is about the same as the denominator.
Round the fraction \(\frac{9}{10}\) to __________.
Remember
A fraction with the same numerator and denominator, such as \(\frac{2}{2}, \frac{5}{5}, \frac{12}{12}\) or \(\frac{96}{96}\), is equal to 1.
STEP 2:
Round \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Think: The numerator is about half the denominator.
Round the fraction \(\frac{5}{8}\) to ___________.
STEP 3:
Subtract
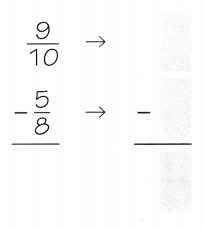
So, \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) is about __________.
Answer:
STEP 1:
Round \(\frac{9}{10}\).
Think: The numerator is about the same as the denominator.
Round the fraction \(\frac{9}{10}\) to \(\frac{10}{10}\)
Remember
A fraction with the same numerator and denominator, such as \(\frac{2}{2}, \frac{5}{5}, \frac{12}{12}\) or \(\frac{96}{96}\), is equal to 1.
STEP 2:
Round \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Think: The numerator is about half the denominator.
Round the fraction \(\frac{5}{8}\) to \(\frac{4}{8}\)
STEP 3:
Subtract
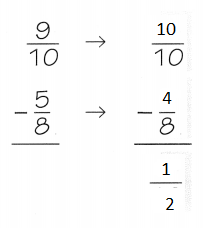
So, \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) is about \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Math Talk
Mathematical Processes
Explain another way you could use benchmarks to estimate \(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\).
Answer:
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
\(\frac{1}{6}\) is very near to \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
Used bench marks to find the sum
Share and Show
Estimate the sum or difference.
Question 1.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
a. Round \(\frac{5}{6}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{6}{6}\)
b. Round \(\frac{3}{8}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{6}{6}\) +\(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 2.
\(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Answer:
a. Round \(\frac{5}{9}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{5}{9}\)
b. Round \(\frac{3}{8}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{18}\)
Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{18}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 3.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer:
a. Round \(\frac{5}{6}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{6}{6}\)
b. Round \(\frac{2}{5}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{6}{6}\) +\(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 4.
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Answer:
a. Round \(\frac{9}{10}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{10}{10}\)
b. Round \(\frac{1}{9}\) to its closest benchmark.
Answer: \(\frac{0}{9}\)
c. Add to find the estimate. \(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{0}{9}\) = 1
Answer: 1
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Problem Solving
Question 5.
How do you know whether your estimate for \(\frac{9}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{6}{7}\) would be greater than or less than the actual sum? Explain.
Answer: Greater than the actual sum
\(\frac{9}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{6}{7}\) =
close to bench marks \(\frac{10}{10}\) + 3\(\frac{7}{7}\) = 4
Explanation:
Is greater than the actual sum
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 6.
Write Math Nick estimated that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) is about 2. Explain how you know his estimate is not reasonable.
Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\)
close to benchmarks \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) = 1
Explanation:
Nick estimated that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) is about 2.
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
so, his estimation is wrong
Problem Solving
Question 7.
Lisa and Valerie are picnicking in Trough Creek State Park in Pennsylvania. Lisa has brought a salad that she made with \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup of strawberries, \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peaches, and \(\frac{1}{6}\) cup of blueberries. About how many total cups of fruit are in the salad?
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) very close to bench marks
\(\frac{4}{4}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{0}{6}\) =2 \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
Lisa and Valerie are picnicking in Trough Creek State Park in Pennsylvania.
Lisa has brought a salad that she made with \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup of strawberries,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peaches, and \(\frac{1}{6}\) cup of blueberries.
2\(\frac{1}{2}\) total cups of fruit are in the salad
Question 8.
Multi-Step At Trace State Park in Mississippi, there is a 40-mile mountain bike trail. Tommy rode A of the trail on Saturday and \(\frac{1}{5}\) of the trail on Sunday. He estimates that he rode more than 22 miles over the two days. Is Tommy’s estimate reasonable?

Answer: yes
Explanation:
\(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 1
20 + 20 = 40
one represents the whole
so, his estimation is reasonable
Question 9.
H.O.T Explain how you know that \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{6}{10}\) is greater than 1.
Answer: No
Explanation:
Close to the bench marks
\(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{10}\) = 1
actual sum is greater than 1
Daily Assessment Task
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.
Question 10.
Mia uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a bag of gravel in the morning and \(\frac{11}{12}\) of a bag in the afternoon. About how much gravel does she use in one day?
(A) 0 bags
(B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) bag
(C) 1 bag
(D) 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) bags
Answer: C
\(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{11}{12}\)
nearest benchmarks are
\(\frac{0}{5}\) + \(\frac{12}{12}\) = 1
Explanation:
Mia uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a bag of gravel in the morning and \(\frac{11}{12}\) of a bag in the afternoon.
she use 1 bag of gravel
Question 11.
Evaluate Reasonableness Hector and Veronica are going hiking. They made a trail mix that has \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup of almonds, \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peanuts, and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of raisins in it. Hector estimates that they made about 3 cups of trail mix. Is the estimate greater than or less than the actual sum? How do you know?
(A) The estimate is greater because each fraction is rounded up to a benchmark.
(B) The estimate is less because each fraction is rounded down to a benchmark.
(C) The estimate is greater because they really made more than 3 cups.
(D) The estimate is less because each fraction is rounded up to a benchmark.
Answer: A
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\)
rounded to nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{3}{3}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{5}\) = 3
Evaluated Reasonableness Hector and Veronica are going hiking.
They made a trail mix that has \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup of almonds, ”
\(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of peanuts,
and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of raisins in it.
Hector estimates that they made about 3 cups of trail mix.
Question 12.
Multi-Step Amanda picked \(\frac{3}{5}\) pound of blueberries at her local farm yesterday. She used \(\frac{3}{8}\) pound of blueberries. Today she picked \(\frac{4}{5}\) pound of blueberries. About how many pounds of blueberries does Amanda have now?
(A) \(\frac{1}{5}\)lb
(B) 1 lb
(C) \(\frac{1}{2}\)lb
(D) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)lbs
Answer: B
Explanation:
what she bought is that she used yesterday
in today marked to nearest benchmarks \(\frac{4}{5}\) is \(\frac{5}{5}\)
that is 1
Texas Test Prep
Question 13.
Jake added \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of sunflower seeds and \(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of banana chips to his sundae. Which is the best estimate of the total amount of toppings Jake added to his sundae?
(A) about 2 cups
(B) about 1 cup
(C) about 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) cups
(D) about \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup
Answer: B
Explanation:
Jake added \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of sunflower seeds and
\(\frac{4}{5}\) cup of banana chips to his sundae.
The best estimate of the total amount of toppings Jake added to his sundae is 1 cup
Texas Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 5.3 Homework and Practice Answer Key
Estimate the sum or difference.
Question 1.
\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{5}\) = 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 2.
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 3.
\(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 4.
\(\frac{6}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{7}{7}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 5.
\(\frac{3}{8}\) – \(\frac{1}{6}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{8}\) – \(\frac{1}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{4}{8}\) – \(\frac{0}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 6.
\(\frac{7}{12}\) + \(\frac{1}{7}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{12}\) + \(\frac{1}{7}\) rounded to the nearest bench marks
\(\frac{6}{12}\) + \(\frac{0}{7}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 7.
\(\frac{4}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{5}{9}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 0
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 8.
\(\frac{1}{9}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{9}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark
\(\frac{0}{9}\) + \(\frac{6}{6}\) = 1
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 9.
\(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) rounded to the nearest bench mark
\(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{7}\) =1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 10.
\(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark
\(\frac{0}{5}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 11.
\(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{2}{6}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{2}{6}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark
\(\frac{9}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 12.
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) = ___________
Answer:
\(\frac{9}{10}\) – \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to the bench marks
\(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 0
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 13.
Explain how you can estimate the sum of \(\frac{4}{5}\) and \(\frac{1}{6}\).
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) rounded to the nearest bench marks
\(\frac{5}{5}\) + \(\frac{0}{6}\) = 1
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Problem Solving
Question 14.
Jena uses \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of raisins for muffins and \(\frac{5}{8}\) cup of raisins for a bowl of oatmeal. Does lena need more than or less than 1 cup of raisins to make muffins and oatmeal? Explain.
Answer: more than 1 cup of raisins
Explanation:
Jena uses \(\frac{7}{8}\) cup of raisins for muffins and
\(\frac{5}{8}\) cup of raisins for a bowl of oatmeal.
\(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded the benhmark
\(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15.
A group of students ate \(\frac{5}{12}\) of a cheese pizza, \(\frac{7}{8}\) of a pepperoni pizza, and \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a veggie pizza. About how many pizzas were eaten?
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{12}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) rounded to the nearest benchmark
\(\frac{6}{12}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = 2
Explanation:
A group of students ate \(\frac{5}{12}\) of a cheese pizza,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) of a pepperoni pizza,
and \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a veggie pizza.
2 pizzas were eaten in whole.
Lesson Check
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.
Question 16.
On Saturday, the scouts hiked \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile up the mountain. On Sunday, they hiked \(\frac{1}{4}\) mile up the mountain. About how far did the scouts hike up the mountain in all?
(A) \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile
(B) 1 mile
(C) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles
(D) 2 miles
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) rounded to nearest benchmark
\(\frac{5}{5}\) + \(\frac{0}{4}\) is 1 mile
Explanation:
On Saturday, the scouts hiked \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile up the mountain.
On Sunday, they hiked \(\frac{1}{4}\) mile up the mountain.
1 mile far the scouts hike up the mountain in all
Question 17.
Which of the following best describes the difference for \(\frac{11}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\) ?
(A) less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(B) greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(C) greater than 1
(D) greater than 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: A
Explanation:
\(\frac{11}{12}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\) is 0
that is less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 18.
Which sum is greatest? Use estimation to decide.
(A) \(\frac{2}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(B) \(\frac{1}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(C) \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\)
(D) \(\frac{2}{9}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Answer: A
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{7}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = 1
Question 19.
Which statement is not correct? Use estimation to decide.
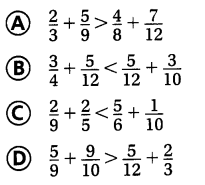
Answer: B
Explanation:
used benchmarks to find reasonable estimates
by rounding fractions to 0, \(\frac{1}{2}\), or 1.
Question 20.
Multi-Step Michaela has \(\frac{11}{12}\) yard of orange fabric and \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard of green fabric. She uses \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard of each color for her sewing project. About how much fabric does Michaela have left if she combines the two colors?
(A) 1 yard
(B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard
(C) 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) yards
(D) 2 yards
Answer: D
\(\frac{11}{12}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to nearest bench marks
\(\frac{12}{12}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 2
Explanation:
2 yards fabric uses Michaela have left if she combines the two colors.
Question 21.
Multi-Step Dustin buys \(\frac{9}{10}\) yard of striped fabric. He uses \(\frac{3}{8}\) yard. He buys \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard more. About how much fabric does Dustin have now?
(A) 1 yard
(B) \(\frac{1}{2}\) yard
(C) 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) yards
(D) 2 yards
Answer: C
Explanation:
Dustin buys \(\frac{9}{10}\) yard of striped fabric.
He uses \(\frac{3}{8}\) yard.
He buys \(\frac{7}{8}\) yard more.
\(\frac{9}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\) rounded to nearest benchmarks
\(\frac{10}{10}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{8}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) yards