Practice questions available in McGraw Hill Math Grade 6 Answer Key PDF Unit Test Lessons 21-23 will engage students and is a great way of informal assessment.
McGraw-Hill Math Grade 6 Unit Test Lessons 21-23 Answer Key
Identify each angle as obtuse, acute, or right.
Question 1.
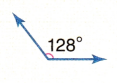
Answer:
obtuse angle
Explanation:
In the above image we can observe an angle 128 degrees. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above angle is obtuse angle.
Question 2.
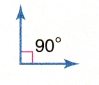
Answer:
Right angle
Explanation:
In the above image we can observe an angle 90 degrees. The angle which measures exactly 90 degrees is called as right angle. So, the above angle is right angle.
Question 3.
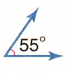
Answer:
Acute angle
Explanation:
In the above image we can observe an angle 55 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above angle is acute angle.
Question 4.
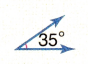
Answer:
Acute angle
Explanation:
In the above image we can observe an angle 35 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above angle is acute angle.
Question 5.
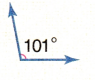
Answer:
obtuse angle
Explanation:
In the above image we can observe an angle 101 degrees. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above angle is obtuse angle.
Identify each pair of angles as supplementary or complementary, and explain why.
Question 6.
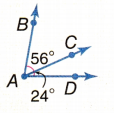
Answer:
The measure of angle ∠DAC is 24°.
The measure of angle ∠CAB is 56°.
∠DAC + ∠CAB = 24° + 56° = 80°
The supplementary angles are two angles that form a line and their sum will be 180°.
The complementary angles are two angles that form a right angle and their sum will be 90°.
So, the above pair of angles are neither supplementary nor complementary..
Question 7.
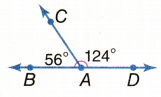
Answer:
The measure of angle ∠CAB is 56°.
The measure of angle ∠DAC is 124°.
∠CAB + ∠DAC = 56° + 124° = 180°
The supplementary angles are two angles that form a line and their sum will be 180°.
The above pair of angles are called as supplementary angles.
Question 8.
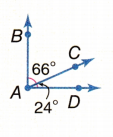
Answer:
The measure of angle ∠CAB is 66°.
The measure of angle ∠DAC is 24°.
∠CAB + ∠DAC = 66° + 24° = 90°
The complementary angles are two angles that form a right angle and their sum will be 90°.
The above pair of angles are called as complementary angles.
Identify each triangle as scalene, equilateral, or isosceles.
Question 9.

Answer:
Isosceles Triangle
Explanation:
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. In the above triangle we can observe two sides having same length and one side having different length. So, the above triangle is isosceles triangle.
Question 10.
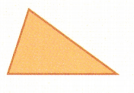
Answer:
Isosceles Triangle
Explanation:
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. In the above triangle we can observe two sides having same length and one side having different length. So, the above triangle is isosceles triangle.
Question 11.

Answer:
Equilateral Triangle
Explanation:
An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. In the above image we can observe the triangle having three sides with a same length. So, the above triangle is equilateral triangle.
Question 12.
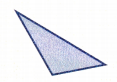
Answer:
Scalene Triangle
Explanation:
A scalene triangle has no sides of equal length. In the above image we can observe the triangle having three sides with a different lengths. So, the above triangle is scalene triangle.
Question 13.

Answer:
Equilateral Triangle
Explanation:
An equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. In the above image we can observe the triangle having three sides with a same length. So, the above triangle is equilateral triangle.
Question 14.

Answer:
Scalene Triangle
Explanation:
A scalene triangle has no sides of equal length. In the above image we can observe the triangle having three sides with a different lengths. So, the above triangle is scalene triangle.
Identify each triangle as obtuse, right, or acute.
Question 15.
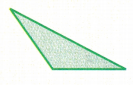
Answer:
Obtuse triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe one obtuse angle. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above triangle is obtuse angle triangle.
Question 16.
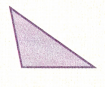
Answer:
Obtuse triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe one obtuse angle. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above triangle is obtuse angle triangle.
Question 17.
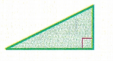
Answer:
Right angle Triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe the angle 90 degrees. The angle which measures exactly 90 degrees is called as right angle. So, the above triangle is right angle triangle.
Question 18.

Answer:
Right angle Triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe the angle 90 degrees. The angle which measures exactly 90 degrees is called as right angle. So, the above triangle is right angle triangle.
Question 19.

Answer:
Acute triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe all the angles are less than 90 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above triangle is acute angle triangle.
Question 20.

Answer:
Acute triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe all the angles are less than 90 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above triangle is acute angle triangle.
Question 21.

Answer:
Obtuse triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe one obtuse angle. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above triangle is obtuse angle triangle.
Question 22.
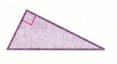
Answer:
Right angle Triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe the angle 90 degrees. The angle which measures exactly 90 degrees is called as right angle. So, the above triangle is right angle triangle.
Question 23.
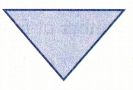
Answer:
Acute triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe all the angles are less than 90 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above triangle is acute angle triangle.
Question 24.
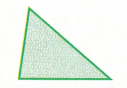
Answer:
Acute triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe all the angles are less than 90 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above triangle is acute angle triangle.
Question 25.

Answer:
Acute triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe all the angles are less than 90 degrees. The angle which measures less than 90 degrees is called as acute angle. So, the above triangle is acute angle triangle.
Question 26.

Answer:
Obtuse triangle
Explanation:
In the above triangle we can observe one obtuse angle. The angle which measures greater than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees is called as obtuse angle. So, the above triangle is obtuse angle triangle.
Identity the following quadrilaterals.
Question 27.

Answer:
The above quadrilateral is Rectangle.
Explanation:
A rectangle is a quadrilateral having four sides. The opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel and equal in length. All the interior angles of rectangle are equal to 90 degrees.
Question 28.

Answer:
The above quadrilateral is Rhombus.
Explanation:
A rhombus is a quadrilateral having four equal sides. The opposite sides of rhombus are parallel to each other.
Question 29.
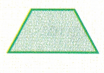
Answer:
The above quadrilateral is Trapezoid.
Explanation:
A trapezoid has four sides and having one pair of parallel sides.
Question 30.

Answer:
The above quadrilateral is Kite.
Explanation:
A kite is a quadrilateral having four sides. Two angles in a kite are equal. Two touching sides are equal in length and the other two touching sides are equal in length.
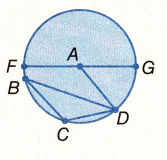
Question 31.
Name the center point.
Answer:
The center point of a circle is A.
Question 32.
Which segments are chords?
Answer:
A chord is a line segment that has both end points on the circumference.
The line segments BD, DC, CB are chords.
Question 33.
Which segment is the diameter?
Answer:
The line segment FG is the diameter.
Question 34.
Which segments are radii?
Answer:
The line segments AG, AF, AD are radii.
A line segment which starts at a circle’s origin and extends to its circumference is called as radius. In circle all radii are equal in length.
Identify each figure and fill in the information requested.
Question 35.
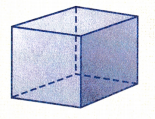
Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Cube
Base is : Square
Number of faces : 6
Number of edges : 12
Number of vertices : 8
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe cube. A cube is a three dimensional solid figure having 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The base of the cube is a square.
Question 36.
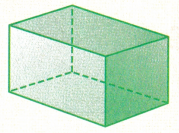
Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Rectangular prism
Base is : Rectangle
Number of faces : 6
Number of edges: 12
Number of vertices : 8
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe rectangular prism. A rectangular prism is a three dimensional solid figure having 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The base of the rectangular prism is rectangle.
Question 37.
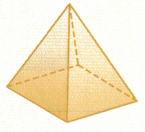
Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Rectangular pyramid
Base is : Rectangle
Number of faces : 5
Number of edges: 8
Number of vertices : 5
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe rectangular pyramid. A rectangular pyramid is a three dimensional solid figure having 5 faces, 8 edges, and 5 vertices. The base of the rectangular pyramid is rectangle.
Question 38.
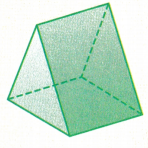
Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Triangular prism
Base is : Rectangle
Number of faces : 5
Number of edges: 9
Number of vertices : 6
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe triangular prism. A triangular prism is a three dimensional solid figure having 5 faces, 9 edges, and 6 vertices. The base of the triangular prism is rectangle.
Question 39.
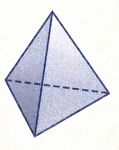
Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Triangular pyramid
Base is : Triangle
Number of faces : 4
Number of edges: 6
Number of vertices : 4
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe triangular pyramid. A triangular pyramid is a three dimensional solid figure having 4 faces, 6 edges, and 4 vertices. The base of the triangular pyramid is triangle.
Question 40.

Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Cone
Base is : Circle
Number of faces : 2
Number of edges: 0
Number of vertices : 1
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe cone. A cone is a three dimensional solid figure having 2 faces, 0 edges, and 1 vertex. The base of the cone is circle.
Question 41.

Figure _______________
Base is _______________
Number of faces _______________
Number of edges _______________
Number of vertices _______________
Answer:
Figure : Cylinder
Base is : Circle
Number of faces : 3
Number of edges: 0
Number of vertices : 0
Explanation:
In the above figure we can observe cylinder. A cylinder is a three dimensional solid figure having 3 faces, 0 edges, and 0 vertices. The base of the cylinder is circle.
Find the surface area of each figure.
Question 42.
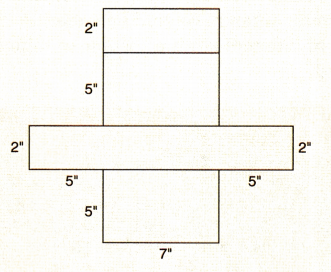
Answer:
Question 43.
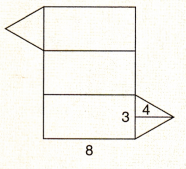
Answer:
Question 44.
Carolyn wants to paint a cube and is trying to figure out the surface area so she knows how much paint to buy. If her cube has sides that measure 4.5 inches, what is the surface area?
Answer:
Given sides of the cube is 4.5 inches.
A cube has 6 square faces.
Surface area of the cube (A) = 6 x s x s
A = 6 x 4.5 in x 4.5 in
A = 121.5 square inches
The surface area of the cube is equal to 121.5 square inches.
Question 45.
Plot the coordinates (1, 1), (6, 1), (1, 6), and (6, 6). Write in the length of each side.
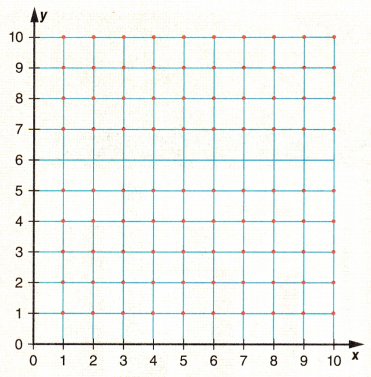
The figure is a _______________
The perimeter is _______________
The area is _______________
Answer:
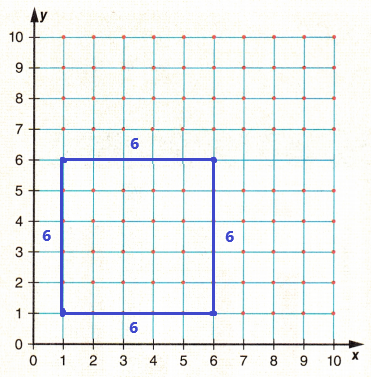
After plotting the given coordinates on the grid, we can observe square in the above figure.
Side of a square s = 6
Perimeter of a square = 4 x s
= 4 x 6
= 24
The perimeter of the square is equal to 24.
Area of square = s x s
= 6 x 6
= 36
The area of the square is equal to 36.