Tired of searching for the best online guide to practice maths? Don’t worry discover all the questions, answers, and explanations on Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles. Free Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles Solution Key PDF is provided to download and practice online. All the students who wish to practice Grade 8 math questions can begin their practice now by using Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key. Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 11 Answer key is the best guide to learn maths.
Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles Answer Key
Students can get trusted results with the practice of Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles. Get unlimited access to Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 11 Questions and Answers on our website. Choose the best and get the best. practice with perfection and get the best results by practicing with Go Math Grade 8 Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles Answer Key.
Lesson 1: Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
- Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal – Page No. 350
- Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal – Page No. 351
- Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal Lesson Check – Page No. 352
Lesson 2: Angle Theorems for Triangles
- Angle Theorems for Triangles – Page No. 358
- Angle Theorems for Triangles – Page No. 359
- Angle Theorems for Triangles Lesson Check – Page No. 360
Lesson 3: Angle-Angle Similarity
- Angle-Angle Similarity – Page No. 366
- Angle-Angle Similarity – Page No. 367
- Angle-Angle Similarity Lesson Check – Page No. 368
Model Quiz
Review
Guided Practice – Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal – Page No. 350
Use the figure for Exercises 1–4.
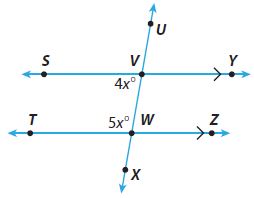
Question 1.
∠UVY and ____ are a pair of corresponding angles.
∠ _________
Answer:
∠ VWZ
Explanation:
∠UVY and ∠ VWZ are a pair of corresponding angles.
When two lines are crossed by Transversal the angles in matching corners are called corresponding angles.
Question 2.
∠WVY and ∠VWT are _________ angles.
____________
Answer:
∠WVY and ∠VWT are alternate interior angles.
Alternate Interior Angles are a pair of angles on the inner side of each of those two lines but on opposite sides of the transversal.
Explanation:
∠WVY and ∠VWT are alternate interior angles.
Alternate Interior Angles are a pair of angles on the inner side of each of those two lines but on opposite sides of the transversal.
Question 3.
Find m∠SVW.
_________ °
Answer:
80º
Explanation:
∠SVW and ∠VWT are same sider interior angles. Therefore,
m∠SVW + m∠VWT = 180º
4xº +5xº = 180º
9x = 180º
x = 180/9
x = 20
m∠SVW = 4xº = (4.20)º = 80º
Question 4.
Find m∠VWT.
_________ °
Answer:
100º
Explanation:
∠SVW and ∠VWT are same sider interior angles. Therefore,
m∠SVW + m∠VWT = 180º
4xº +5xº = 180º
9x = 180º
x = 180/9
x = 20
m∠VWT = 5xº = (5.20)º = 100º
Question 5.
Vocabulary When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, _______________ angles are supplementary.
____________
Answer:
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of alternate exterior angles are congruent. If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of consecutive interior angles are supplementary.
ESSENTIAL QUESTION CHECK-IN
Question 6.
What can you conclude about the interior angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal?
Type below:
____________
Answer:
Alternate interior angles are congruent; same-side interior angles are supplementary.
Explanation:
When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the interior angles will be the angles between the two parallel lines. Alternate interior angles will be on opposite sides of the transversal; the measures of these angles are the same.
Same-side interior angles will be on the same side of the transversal; the measures of these angles will be supplementary, adding up to 180 degrees.
11.1 Independent Practice – Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal – Page No. 351
Vocabulary Use the figure for Exercises 7–10.
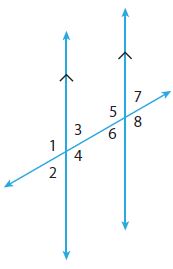
Question 7.
Name all pairs of corresponding angles.
Type below:
____________
Answer:
∠1 and ∠5
∠3 and ∠7
∠2 and ∠6
∠4 and ∠8
Explanation:
Corresponding angles are
∠1 and ∠5
∠3 and ∠7
∠2 and ∠6
∠4 and ∠8
Question 8.
Name both pairs of alternate exterior angles.
Type below:
____________
Answer:
∠1 and ∠8
∠2 and ∠7
Explanation:
Alternate exterior angles
∠1 and ∠8
∠2 and ∠7
Question 9.
Name the relationship between ∠ 3 and ∠6.
Type below:
____________
Answer:
alternate interior angles
Explanation:
∠3 and ∠6 are alternate interior angles.
Alternate Interior Angles are a pair of angles on the inner side of each of those two lines but on opposite sides of the transversal.
Question 10.
Name the relationship between ∠4 and ∠6.
Type below:
____________
Answer:
same-side interior angles
Explanation:
∠4 and ∠6 are same-side interior angles.
Find each angle measure.
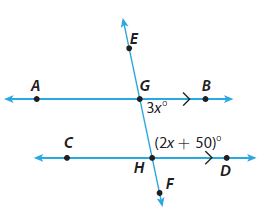
Question 11.
m∠AGE when m∠FHD = 30°
_________ °
Answer:
m∠AGE = 30°
Explanation:
∠AGE and ∠FHD are alternate exterior angles.
Therefore, m∠AGE = m∠FHD = 30°
m∠AGE = 30°
Question 12.
m∠AGH when m∠CHF = 150°
_________ °
Answer:
150°
Explanation:
∠AGH and ∠CHF are corresponding angles.
Therefore, m∠AGH = m∠CHF = 150°
m∠AGH = 150°
Question 13.
m∠CHF when m∠BGE = 110°
_________ °
Answer:
110°
Explanation:
∠CHF and ∠BGE are alternate exterior angles.
Therefore, m∠CHF = m∠BGE = 110°
m∠CHF = 110°
Question 14.
m∠CHG when m∠HGA = 120°
_________ °
Answer:
m∠CHG = 60º
Explanation:
∠CHF and ∠HGA are same-side interior angles.
m∠CHG + m∠HGA = 180°
m∠CHG + 120° = 180°
m∠CHG = 180 – 120 = 60
m∠CHG = 60º
Question 15.
m∠BGH
_________ °
Answer:
78º
Explanation:
∠BGH and ∠GHD are same-side interior angles.
So, ∠BGH + ∠GHD = 180º
3x + (2x + 50)º = 180º
5x = 180º – 50º = 130º
x = 130/5 = 26º
∠BGH = 3xº = 3 × 26º = 78º
∠GHD = (2x + 50) += (2 × 26 + 50) = 102º
Question 16.
m∠GHD
_________ °
Answer:
102º
Explanation:
∠BGH and ∠GHD are same-side interior angles.
So, ∠BGH + ∠GHD = 180º
3x + (2x + 50)º = 180º
5x = 180º – 50º = 130º
x = 130/5 = 26º
∠BGH = 3xº = 3 × 26º = 78º
∠GHD = (2x + 50) += (2 × 26 + 50) = 102º
Question 17.
The Cross Country Bike Trail follows a straight line where it crosses 350th and 360th Streets. The two streets are parallel to each other. What is the measure of the larger angle formed at the intersection of the bike trail and 360th Street? Explain.
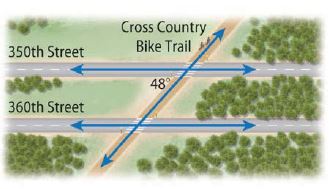
_________ °
Answer:
The larger angle formed at the intersection of the bike trail and 360th Street is 132º
Explanation:
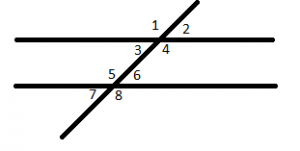
The larger angle formed at the intersection of the bike trail and 360th Street is the angle 5 in our schema. ∠5 and ∠3 are same-side interior angles. Therefore, m∠5 + m∠3 = 180º
m∠5 + 48º = 180º
m∠5 = 180º – 48º
m∠5 = 132º
Question 18.
Critical Thinking How many different angles would be formed by a transversal intersecting three parallel lines? How many different angle measures would there be?
_________ different angles
_________ different angle measures
Answer:
12 different angles
2 different angle measures
Explanation:
There are 12 different angles formed by a transversal intersecting three parallel lines.
There are 2 different angle measures:
m∠1 = m∠4 = m∠5 = m∠8 = m∠9 = m∠12
m∠2 = m∠3 = m∠6 = m∠7 = m∠10 = m∠11
Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal – Page No. 352
Question 19.
Communicate Mathematical Ideas In the diagram at the right, suppose m∠6 = 125°. Explain how to find the measures of each of the other seven numbered angles.
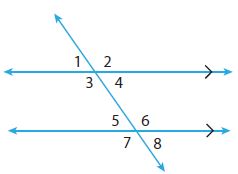
Type below:
____________
Answer:
m∠2 = m∠6 = 125º because ∠2 and ∠6 are corresponding angles.
m∠3 = m∠2 = 125º because ∠3 and ∠2 are vertical angles.
m∠7 = m∠3 = 125º because ∠7 and ∠3 are corresponding angles.
∠4 and ∠6 are same-side interior angles.
Therefore, m∠4 + m∠6 = 180º
m∠4 + 125º = 180º
m∠4 = 180º – 125º
m∠4 = 55º
m∠8 = m∠4 = 55º because ∠8 and ∠4 are corresponding angles.
m∠1 = m∠4 = 55º because ∠1 and ∠4 are vertical angles.
m∠5 = m∠1 = 55º because ∠5 and ∠1 are corresponding angles.
FOCUS ON HIGHER ORDER THINKING
Question 20.
Draw Conclusions In a diagram showing two parallel lines cut by a transversal, the measures of two same-side interior angles are both given as 3x°. Without writing and solving an equation, can you determine the measures of both angles? Explain. Then write and solve an equation to find the measures.
Answer:
m∠1 and m∠2 are same-side interior angles is 180º
Therefore, m∠1 + m∠2 = 180º
3x + 3x = 180º
6x = 180º
x = 180/6 = 30
m∠1 = m∠2 = 3x = 3(30) = 90º
Question 21.
Make a Conjecture Draw two parallel lines and a transversal. Choose one of the eight angles that are formed. How many of the other seven angles are congruent to the angle you selected? How many of the other seven angles are supplementary to your angle? Will your answer change if you select a different angle?
Type below:
____________
Answer:
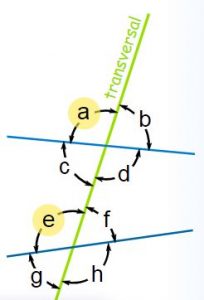
We have to select ∠a form of eight angles that are formed. There are two other angles that are congruent to the angle ∠a. Two other angles are ∠e and ∠g.
There are no supplementary to ∠a.
If we select a different angle then the answer will also change.
Question 22.
Critique Reasoning In the diagram at the right, ∠2, ∠3, ∠5, and∠8 are all congruent, and∠1, ∠4, ∠6, and ∠7 are all congruent. Aiden says that this is enough information to conclude that the diagram shows two parallel lines cut by a transversal. Is he correct? Justify your answer.
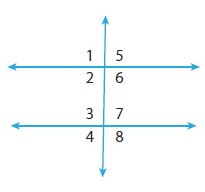
____________
Answer:
This is not enough information to conclude that the diagram shows two parallel lines cut by a transversal. Because ∠2 and ∠3 are same-side interior angles. But ∠5 and ∠8 are not congruent with each other. And ∠6 and ∠7 are same-side interior angles. But ∠1 and ∠4 are not congruent with each other.
Guided Practice – Angle Theorems for Triangles – Page No. 358
Find each missing angle measure.
Question 1.
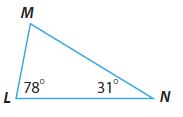
m∠M = _________ °
Answer:
m∠M = 71º
Explanation:
From the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠L + m∠N + m∠M = 180º
78º + 31º + m∠M = 180º
109º + m∠M = 180º
m∠M = 180º – 109º
m∠M = 71º
Question 2.
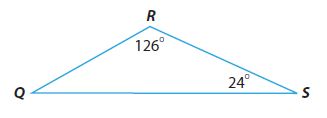
m∠Q = _________ °
Answer:
m∠Q = 30º
Explanation:
From the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠Q + m∠S + m∠R = 180º
m∠Q + 24º + 126º = 180º
m∠Q + 150º = 180º
m∠Q = 180º – 150º
m∠Q = 30º
Use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find the measure of each angle in degrees.
Question 3.
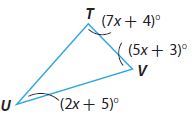
m∠T = _________ °
m∠V = _________ °
m∠U = _________ °
Answer:
m∠T = 88°
m∠V = 63°
m∠U = 29°
Explanation:
From the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠U + m∠T + m∠V = 180º
(2x + 5)º + (7x + 4)º + (5x + 3)º = 180º
2xº + 5º + 7xº + 4º + 5xº + 3º = 180º
14xº + 12º = 180º
14xº = 168º
x = 168/14 = 12
Substitute x value to find the angles
m∠U = (2x + 5)º = ((2 . 12) + 5)º = 29º
m∠U = 29º
m∠T = (7x + 4)º = ((7 . 12) + 4)º = 88º
m∠T = 88º
m∠V = (5x + 3)º = ((5 . 12) + 3)º = 63º
m∠V = 63º
Question 4.
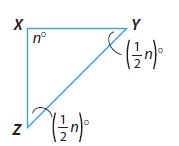
m∠X = _________ °
m∠Y = _________ °
m∠Z = _________ °
Answer:
m∠X = 90°
m∠Y = 45 °
m∠Z = 45°
Explanation:
From the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠X + m∠Y + m∠Z = 180º
nº + (1/2 . n)º + (1/2 . n)º = 180º
2nº = 180º
n = 90
Substitute n values to find the angles
m∠X = nº = 90º
m∠X = 90º
m∠Y = (1/2 . n)º = (1/2 . 90)º = 45º
m∠Y = 45º
m∠Z = (1/2 . n)º = (1/2 . 90)º = 45º
m∠Z = 45º
Use the Exterior Angle Theorem to find the measure of each angle in degrees.
Question 5.
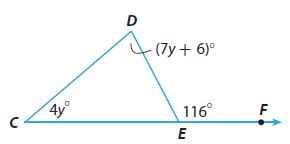
m∠C = _________ °
m∠D = _________ °
Answer:
m∠C = 40°
m∠D = 76°
Explanation:
Given m∠C = 4y°, m∠D = (7y + 6)°, m∠E = 116°
By using exterior angle theorem,
∠DEC + ∠DEF = 180°
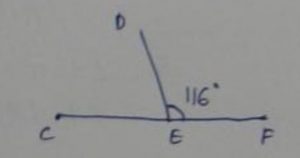
∠DEC + 116° = 180°
∠E = ∠DEC = 180° – 116° = 64°
The sum of the angles of a traingle = 180°
∠C +∠D + ∠E = 180°
4y° + (7y + 6)°+ 64° = 180°
11y° + 70° = 180°
11y° = 180° – 70° = 110°
y = 10
∠C = 4y° = 4. 10 = 40°
∠D = (7y + 6)° = ((7 . 10) + 6)° = (70 + 6)° = 76°
Question 6.
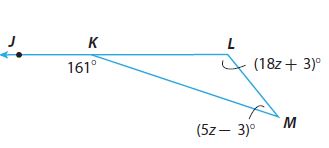
m∠L = _________ °
m∠M = _________ °
Answer:
m∠L = 129°
m∠M = 32°
Explanation:
Given that m∠M = (5z – 3)°, m∠L = (18z + 3)°, m∠JKM = 161°
From the Exterior Angle Theorem,
m∠M + m∠L = m∠JKM
(5z – 3)° + (18z + 3)° = 161°
5z° – 3° + 18z° + 3° = 161°
23z° = 161°
z = 161/23 = 7
Substitute z values to find the angles
m∠M = (5z – 3)° = ((5 . 7) – 3)° = 32°
m∠L = (18z + 3)° = ((18 . 7) + 3)° = 129°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠M + m∠L + m∠LKM = 180º
32º + 129º + m∠LKM = 180º
161º + m∠LKM = 180º
m∠LKM = 19º
ESSENTIAL QUESTION CHECK-IN
Question 7.
Describe the relationships among the measures of the angles of a triangle.
Type below:
______________
Answer:
The sum of all measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of its remote interior angles.
11.2 Independent Practice – Angle Theorems for Triangles – Page No. 359
Find the measure of each angle.
Question 8.
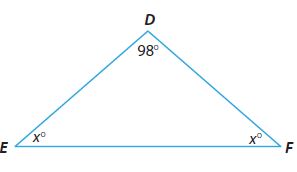
m∠E = _________ °
m∠F = _________ °
Answer:
m∠E = 41°
m∠F = 41°
Explanation:
m∠E = x°, m∠F = x°, m∠D = 98°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, sum of the angles of the traingle is 180°
m∠E + m∠D + m∠F = 180°
x + 98 + x = 180°
2x + 98 = 180°
2x = 82°
x = 41°
So, m∠E = 41°
m∠F = 41°
Question 9.
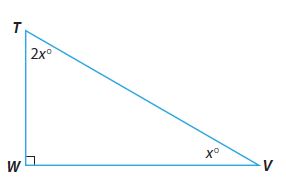
m∠T = _________ °
m∠V = _________ °
Answer:
m∠T = 60°
m∠V = 30°
Explanation:
m∠W = 90°, m∠T = 2x°, m∠V = x°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, sum of the angles of the traingle is 180°
m∠T + m∠V + m∠W = 180°
2x + x + 90 = 180°
3x = 90°
x = 30°
So, m∠T = 2x° = 2 . 30° = 60°
m∠V = x° = 30°
Question 10.
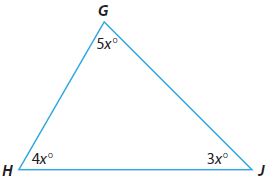
m∠G = _________ °
m∠H = _________ °
m∠J = _________ °
Answer:
m∠G = 75°
m∠H = 60°
m∠J = 45°
Explanation:
m∠G = 5x°, m∠H = 4x°, m∠J = 3x°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, sum of the angles of the traingle is 180°
m∠G + m∠H + m∠J = 180°
5x + 4x + 3x = 180°
12x = 90°
x = 15°
So, m∠G = 5x° = 5 . 15° = 75°
m∠H = 4x° = 4. 15° = 60°
m∠J = 3x° = 3. 15° = 45°
Question 11.
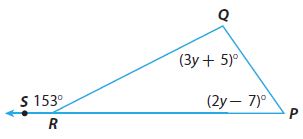
m∠Q = _________ °
m∠P = _________ °
m∠QRP = _________ °
Answer:
m∠Q = 98°
m∠P = 55°
m∠QRP = 27°
Explanation:
Given that m∠Q = (3y + 5)°, m∠P = (2y – 7)°, m∠QRS = 153°
From the exterior angle Theorem,
∠QRS + ∠QRP = 180°
153° + ∠QRP = 180°
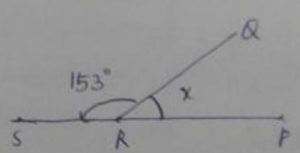
m∠R = m∠QRP = 180° – 153° = 27°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°
m∠P + m∠Q + m∠R = 180°
(3y + 5)° + (2y – 7)°+ 27° = 180°
5y° + 25 = 180°
5y° = 155°
y = 31°
m∠Q = (3y + 5)° = ((3 . 31°) + 5)° = 98°
m∠P = (2y – 7)° = ((2. 31° – 7)° = 55°
m∠QRP = 27°
Question 12.
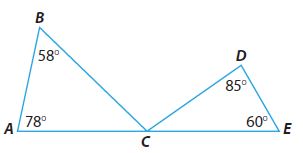
m∠ACB = _________ °
m∠DCE = _________ °
m∠BCD = _________ °
Answer:
m∠ACB = 44°
m∠DCE = 35°
m∠BCD = 101°
Explanation:
In traingle ABC, m∠A = 78°, m∠B = 58°, m∠ACB = ?°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°
m∠A + m∠B + m∠ACB = 180°
78° + 58° + m∠ACB = 180°
m∠ACB = 180° – 136°
m∠ACB = 44°
In traingle CDE, m∠D = 85°, m∠E = 60°, m∠CDE = ?°
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°
m∠D + m∠E + m∠CDE = 180°
85° + 60° + m∠CDE = 180°
m∠CDE = 180° – 145°
m∠CDE = 35°
From the Exterior Angle Theorem,
m∠ACB + m∠CDE + m∠BCD = 180°
44° + 35° + m∠BCD = 180°
m∠BCD = 180° – 79°
m∠BCD = 101°
Question 13.
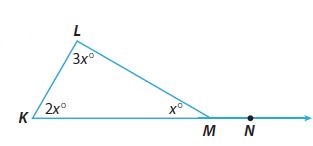
m∠K = _________ °
m∠L = _________ °
m∠KML = _________ °
m∠LMN = _________ °
Answer:
Explanation:
m∠K = 2x°, m∠L = 3x°, m∠KML = x°
So, From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°.
m∠K + m∠L + m∠KML = 180°
2x° + 3x° + x° = 180°
6x° = 180°
x= 30°
∠KML = x = 30°
∠L = 3x = 3 . 30° = 90°
∠K = 2x = 2 . 30° = 60°
From the Exterior Angle Theorem,
∠KML + ∠LMN = 180°
∠LMN = 180° – 30° = 150°
Question 14.
Multistep The second angle in a triangle is five times as large as the first. The third angle is two-thirds as large as the first. Find the angle measures.
The measure of the first angle: _________ °
The measure of the second angle: _________ °
The measure of the third angle: _________ °
Answer:
The measure of the first angle: 27°
The measure of the second angle: 135°
The measure of the third angle: 18°
Explanation:
Let us name the angles of a triangle as ∠1, ∠2, ∠3.
Consider ∠1 as x.
∠2 is 5 times as large as the first.
∠2 = 5x
Also, ∠3 = 2/3 . x
So, From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°.
x+ 5x + (2/3 . x) = 180°
20x = 540°
x = 27°
So, ∠1 = x = 27°
∠2 = 5x = 5 . 27° = 135°
∠3 = 2/3 . x = 2/3 . 27° = 18°
The measure of the first angle: 27°
The measure of the second angle: 135°
The measure of the third angle: 18°
Angle Theorems for Triangles – Page No. 360
Question 15.
Analyze Relationships Can a triangle have two obtuse angles? Explain.
___________
Answer:
No; a triangle can NOT have two obtuse angles
Explanation:
The measure of an obtuse angle is greater than 90°. Two obtuse angles and the third angle would have a sum greater than 180°
FOCUS ON HIGHER ORDER THINKING
Question 16.
Critical Thinking Explain how you can use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find the measures of the angles of an equilateral triangle.
Type below:
___________
Answer:
All angles have the same measure in an equilateral triangle
Explanation:
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
∠x + ∠x + ∠x = 180°
3∠x = 180°
∠x = 60°
All angles have the same measure in an equilateral triangle
Question 17.
a. Draw Conclusions Find the sum of the measures of the angles in quadrilateral ABCD. (Hint: Draw diagonal \(\overline { AC } \). How can you use the figures you have formed to find the sum?)
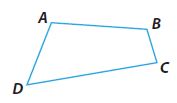
Sum: _________ °
Answer:
Sum: 360°
Question 17.
b. Make a Conjecture Write a “Quadrilateral Sum Theorem.” Explain why you think it is true.
Type below:
___________
Answer:
The sum of the angle measures of a quadrilateral is 360°
Any quadrilateral can be divided into two triangles (180 + 180 = 360)
Question 18.
Communicate Mathematical Ideas Describe two ways that an exterior angle of a triangle is related to one or more of the interior angles.
Type below:
___________
Answer:
An exterior angle and it’s an adjacent interior angle equal 180°
An exterior angle equals the sum of the two remote interior angles.
Guided Practice – Angle-Angle Similarity – Page No. 366
Question 1.
Explain whether the triangles are similar. Label the angle measures in the figure.
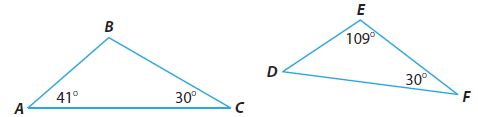
Type below:
___________
△ABC has angle measures _______and △DEF has angle measures______. Because _______in one triangle are congruent to ______in the other triangle, the triangles are_____.
Answer:
△ABC has angle measures 40°, 30°, and 109° and △DEF has angle measures 41°, 109°, and 30°. Because 2∠s in one triangle are congruent to in the other triangle, the triangles similar.
Question 2.
A flagpole casts a shadow 23.5 feet long. At the same time of day, Mrs. Gilbert, who is 5.5 feet tall, casts a shadow that is 7.5 feet long. How tall in feet is the flagpole? Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
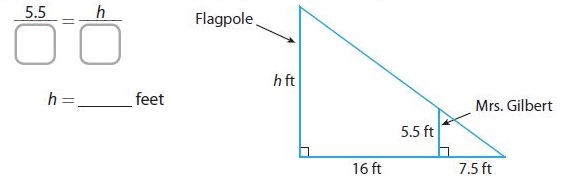
_________ ft
Answer:
17.2 ft
Explanation:
In similar triangles, corresponding side lengths are proportional.
5.5/7.5 = h/23.5
h (7.5) = 129.25
h = 129.25/7.5
h = 17.23
Rounding to the nearest tenth
h = 17.2 feet
Question 3.
Two transversals intersect two parallel lines as shown. Explain whether △ABC and △DEC are similar.
∠BAC and∠EDC are ___________ since they are ___________.
∠ABC and∠DEC are ___________ since they are ___________.
By ________, △ABC and△DEC are ___________.
Type below:
___________
Answer:
∠BAC and∠EDC are congruent since they are alt. interior ∠s
∠ABC and∠DEC are congruent since they are alt. interior ∠s.
By AA similarity, △ABC and△DEC are similar.
ESSENTIAL QUESTION CHECK-IN
Question 4.
How can you determine when two triangles are similar?
Type below:
___________
Answer:
If 2 angles of one triangle are congruent to 2 angles of another triangle, the triangles are similar by the Angle-Angle Similarity Postulate
11.3 Independent Practice – Angle-Angle Similarity – Page No. 367
Use the diagrams for Exercises 5–7.
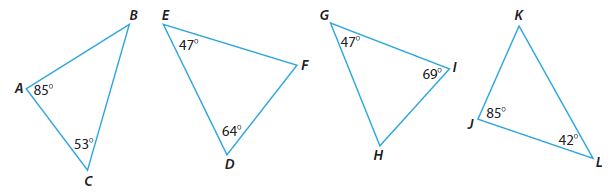
Question 5.
Find the missing angle measures in the triangles.
Type below:
___________
Answer:
m∠B = 42°
m∠F = 69°
m∠H = 64°
m∠K = 53°
Explanation:
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180°
85° + m∠B + 53° = 180°
138° + m∠B = 180°
m∠B = 180° – 138°
m∠B = 42°
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠D + m∠E + m∠F = 180°
We substitute the given angle measures and we solve for m∠F
64° + 47° + m∠F = 180°
111° + m∠F = 180°
m∠F = 180° – 111°
m∠F = 69°
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠G + m∠H + m∠J = 180°
We substitute the given angle measures and we solve for m∠H
47° + m∠H + 69° = 180°
116° + m∠H = 180°
m∠H = 180° – 116°
m∠H = 64°
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠J + m∠K + m∠L = 180°
We substitute the given angle measures and we solve for m∠K
85° + m∠K + 42° = 180°
127° + m∠K = 180°
m∠K = 180° – 127°
m∠K = 53°
Question 6.
Which triangles are similar?
Type below:
___________
Answer:
△ABC and △JKL are similar because their corresponding angles are congruent. Also, △DEF and △GHJ are similar because their corresponding is congruent.
Question 7.
Analyze Relationships Determine which angles are congruent to the angles in △ABC.
∠A ≅ ∠ ________
∠B ≅ ∠ ________
∠C ≅ ∠ ________
Answer:
△JKL ≅ △ABC
Explanation:
△JKL has angle measures that are the same as those is △ABC
∠A ≅ ∠ J
∠B ≅ ∠ L
∠C ≅ ∠ K
Therefore, they are congruent.
Question 8.
Multistep A tree casts a shadow that is 20 feet long. Frank is 6 feet tall,and while standing next to the tree he casts a shadow that is 4 feet long.
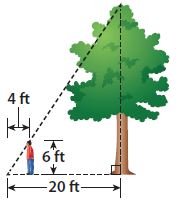
a. How tall is the tree?
h = ________ ft
Answer:
h = 30 ft
Explanation:
In similar triangles, corresponding side lengths are proportional.
20/4 = h/6
5 = h/6
h = 30
The tree is 30 feet tall.
Question 8.
b. How much taller is the tree than Frank?
________ ft
Answer:
24 ft
Explanation:
30 – 6 = 24
The tree is 24 feet taller than Frank.
Question 9.
Represent Real-World Problems Sheila is climbing on a ladder that is attached against the side of a jungle gym wall. She is 5 feet off the ground and 3 feet from the base of the ladder, which is 15 feet from the wall. Draw a diagram to help you solve the problem. How high up the wall is the top of the ladder?
________ ft
Answer:
25 ft
Explanation:
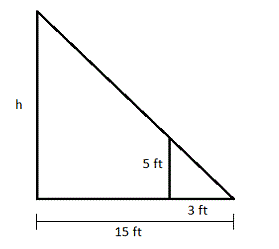
3/15 = 5/h
15 ×3 = 3h
75 = 3h
h = 75/3 = 25
Question 10.
Justify Reasoning Are two equilateral triangles always similar? Explain.
______________
Answer:
yes; two equilateral triangles are always similar.
Each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°. Since both triangles are equilateral then they are similar.
Angle-Angle Similarity – Page No. 368
Question 11.
Critique Reasoning Ryan calculated the missing measure in the diagram shown. What was his mistake?
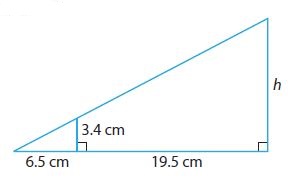
\(\frac{3.4}{6.5}=\frac{h}{19.5}\)
19.5 × \(\frac{3.4}{6.5}=\frac{h}{19.5}\) × 19.5
\(\frac{66.3}{6.5}\) = h
10.2cm = h
Type below:
___________
Answer:
In the first line, Ryan did not take the sum of 6.5 and 19.5 to get the denominator on the right.
The denominator on the right should be 26 instead of 19.5
the correct value for h
3.4/6.5 = h/26
h = (3.4/6.5) × 26
h = 13.6cm
FOCUS ON HIGHER ORDER THINKING
Question 12.
Communicate Mathematical Ideas For a pair of triangular earrings, how can you tell if they are similar? How can you tell if they are congruent?
Type below:
___________
Answer:
The earrings are similar if two angle measures of one are equal to two angle measures of the other.
The earrings are congruent if they are similar and if the side lengths of one are equal to the side lengths of the other.
Question 13.
Critical Thinking When does it make sense to use similar triangles to measure the height and length of objects in real life?
Type below:
___________
Answer:
If the item is too tall or the distance is too long to measure directly, similar triangles can help with measuring.
Question 14.
Justify Reasoning Two right triangles on a coordinate plane are similar but not congruent. Each of the legs of both triangles are extended by 1 unit, creating two new right triangles. Are the resulting triangles similar? Explain using an example.
___________
Answer:
Two triangles are similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the lengths of their corresponding sides are proportional. If each of the legs of both triangles is extended by 1 unit, the ratio between proportional sides does not change. Therefore, the resulting triangles are similar.
Ready to Go On? – Model Quiz – Page No. 369
11.1 Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
In the figure, line p || line q. Find the measure of each angle if m∠8 = 115°.
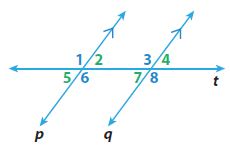
Question 1.
m∠7 = _________ °
Answer:
m∠7 = 65°
Explanation:
According to the exterior angle theorem,
m∠7 + m∠8 = 180°
m∠7 + 115° = 180°
m∠7 = 180° – 115°
m∠7 = 65°
Question 2.
m∠6 = _________ °
Answer:
m∠6 = 115°
Explanation:
From the given figure, Line P is parallel to line Q. So, the angles given in line P is equal to the angles in line Q. They are corresponding angles.
So, m∠8 is parallel is m∠6 or m∠8 = m∠6 = 115°
Question 3.
m∠1 = _________ °
Answer:
m∠1 = 115°
Explanation:
∠1 and ∠6 are alternative exterior angles.
So, m∠1 = m∠6 = 115°
11.2 Angle Theorems for Triangles
Find the measure of each angle.
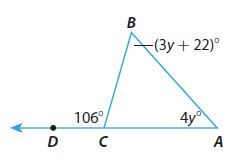
Question 4.
m∠A = _________ °
Answer:
m∠A = 48°
Explanation:
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180°
4y° + (3y + 22)° + 74° = 180°
7y = 180 – 96 = 84
y = 12°
m∠A = 4y° = 4 (12°) = 48°
m∠B = (3y + 22)° = (3(12°) + 22)° = 58°
Question 5.
m∠B = _________ °
Answer:
m∠B = 58°
Explanation:
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180°
4y° + (3y + 22)° + 74° = 180°
7y = 180 – 96 = 84
y = 12°
m∠A = 4y° = 4 (12°) = 48°
m∠B = (3y + 22)° = (3(12°) + 22)° = 58°
Question 6.
m∠BCA = _________ °
Answer:
m∠BCA = 74°
Explanation:
m∠BCD + m∠BCA = 180°
106° + m∠BCA = 180°
m∠BCA = 180° – 106°
m∠BCA = 74°
So, m∠BCA = 74°
11.3 Angle-Angle Similarity
Triangle FEG is similar to triangle IHJ. Find the missing values.
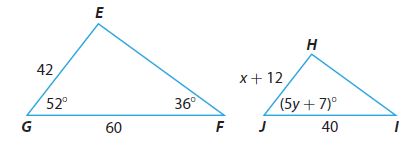
Question 7.
x = _________
Answer:
x = 16
Explanation:
In similar triangles, corresponding side lengths are proportional.
HJ/EG = IJ/FG
(x + 12)/42 = 40/60
(x + 12)/42 = 4/6
6x = 96
x = 16
Question 8.
y = _________
Answer:
y = 9
Explanation:
In similar triangles, corresponding side lengths are congruent.
m∠HJI = m∠EGF
(5y + 7)° = 52°
5y° + 7° = 52°
5y° = 45°
y = 9
Question 9.
m∠H = _________°
Answer:
m∠H = 92°
Explanation:
Using the Triangle Sum Theorem,
m∠E + m∠F + m∠G = 180°
We substitute the given angle measures and we solve for m∠E
m∠E + 36° + 52° = 180°
m∠E + 88° = 180°
m∠E = 92°
In similar angles, corresponding side lengths are congruent
m∠H = m∠E
m∠H = 92°
ESSENTIAL QUESTION
Question 10.
How can you use similar triangles to solve real-world problems?
Type below:
____________
Answer:
we know that if two triangles are similar, then their corresponding angles are congruent and the lengths of their corresponding sides are proportional. We can use this to determine values that we cannot measure directly. For example, we can calculate the length of the tree if we measure its shadow and our shadow on a sunny day.
Selected Response – Mixed Review – Page No. 370
Use the figure for Exercises 1 and 2.
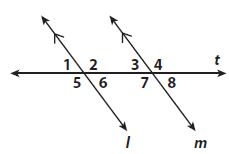
Question 1.
Which angle pair is a pair of alternate exterior angles?
Options:
A. ∠5 and ∠6
B. ∠6 and∠7
C. ∠5 and ∠4
D. ∠5 and ∠2
Answer:
C. ∠5 and ∠4
Explanation:
∠5 and ∠4 are alternate exterior angles
Question 2.
Which of the following angles is not congruent to ∠3?
Options:
A. ∠1
B. ∠2
C. ∠6
D. ∠8
Answer:
B. ∠2
Explanation:
∠2 and ∠3 are same-side interior angles. They are not congruent instead their sum is equal to 180°
Question 3.
The measures, in degrees, of the three angles of a triangle are given by 2x + 1, 3x – 3, and 9x. What is the measure of the smallest angle?
Options:
A. 13°
B. 27°
C. 36°
D. 117°
Answer:
B. 27°
Explanation:
From the Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the angles of the triangle is 180°
m∠1 + m∠2 + m∠3 = 180°
(2x + 1)° + (3x – 3)° + (9x)° = 180°
2x° + 1° + 3x° – 3° + 9x° = 180°
14x° – 2° = 180°
14x° = 178°
x = 13
Substitute the value of x to find the m∠1, m∠2, and m∠3
m∠1 = (2x + 1)° = (2(13) + 1)° = 27°
m∠2 = (3x – 3)° = (3(13) – 3)° = 36°
m∠3 = (9x)° = (9(13))° = 117°
The smallest angle is 27°
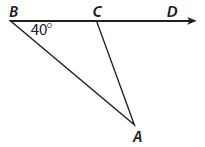
Question 4.
Which is a possible measure of ∠DCA in the triangle below?
Options:
A. 36°
B. 38°
C. 40°
D 70°
Answer:
D 70°
Explanation:
Using the Exterior Angle Theorem
m∠A + m∠B = m∠DCA
m∠A + 40° = m∠DCA
m∠DCA will be greater than 40°. The only suitable option is D, 70°.
Question 5.
Kaylee wrote in her dinosaur report that the Jurassic period was 1.75 × 108 years ago. What is this number written in standard form?
Options:
A. 1,750,000
B. 17,500,000
C. 175,000,000
D. 17,500,000,000
Answer:
C. 175,000,000
Explanation:
1.75 × 108 standard form
Move the decimal point to 8 right places.
175,000,000
Question 6.
Given that y is proportional to x, what linear equation can you write if y is 16 when x is 20?
Options:
A. y = 20x
B. y = \(\frac{5}{4}\) x
C. y = \(\frac{4}{5}\)x
D. y = 0.6x
Answer:
C. y = \(\frac{4}{5}\)x
Explanation:
Y=4/5x
16=4/5(20)
4/5×20/1=80/5
80/5=16
Mini-Task
Question 7.
Two transversals intersect two parallel lines as shown.
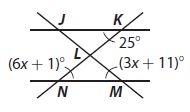
a. What is the value of x?
x = ________
Answer:
x = 4
Explanation:
m∠JKL = m∠LNM
6x + 1 = 25
6x = 24
x = 4
Question 7.
b. What is the measure of ∠LMN?
_________°
Answer:
23°
Explanation:
m∠LMN = 3x + 11 = 3(4) + 11 = 12 + 11 = 23
Question 7.
c. What is the measure of ∠KLM?
∠KLM = _________°
Answer:
∠KLM = 48°
Explanation:
∠KLM exterior angle of the triangle LMN
m∠KLM = m∠LNM + m∠LMN
= 25 + 23 = 48
Question 7.
d. Which two triangles are similar? How do you know?
Type below:
_____________
Answer:
triangle JKL = triangle LNM
triangle KJL = triangle LMN
Explanation:
triangle JLK and triangle LNM are similar.
triangle JKL = triangle LNM
triangle KJL = triangle LMN
Conclusion:
Go Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 11 Angle Relationships in Parallel Lines and Triangles PDF for the best practice. Practice all the math questions available on Grade 8 Text Book and learn how to solve Grade 8 math questions in a simple way.
